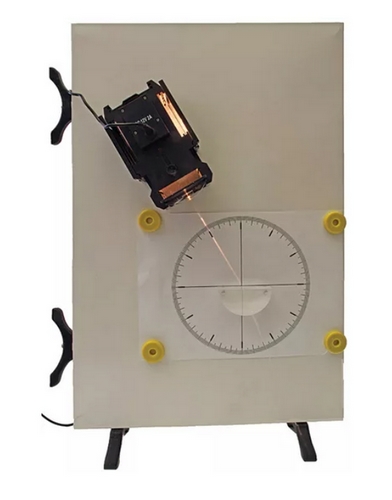
Optical Experiment Set Lens Set Magnetic with Light Box
9.005,00 ₺ (Türkçe) KDV dahil
Only 2 left in stock
Description
- Import of ECE
- Compatible with the curriculum
- Suitable for school, experiment, project work
- It can be used in optics lectures, optical experiments, etc.
- Create single or multiple parallel, convergent or divergent beams.
- Blend up to three colors on a screen to study color mixing.
- Create and test complex light paths from theoretical layouts.
- Perform many more light and color experiments.
Product Content:
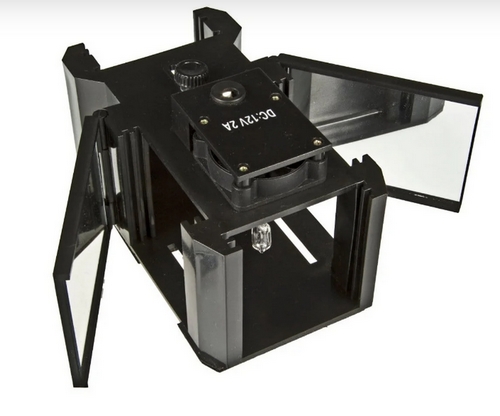
Light box:
- Dimensions: 15 cm x 9.5 cm x 8.8 cm (6” x 3¾” x 3½”) with mirrors closed
- Mirror size: 9 cm x 6.4 cm (3⅝” x 2½”)
- Weight: 340 g (0.75 lb)
- Lamp: 12V d.c./20W halogen lamp with adjustable holder for focus
- Built-in 12V d.c. cooling fan
- Magnetic base for attachment to steel-based surfaces
- Wall-mounted power supply for 110VAC input with 1.5 m (5’) cord
- Provision for two 62 mm x 62 mm (2⅜”) filters in each of four apertures and a cylindrical lens at one end.
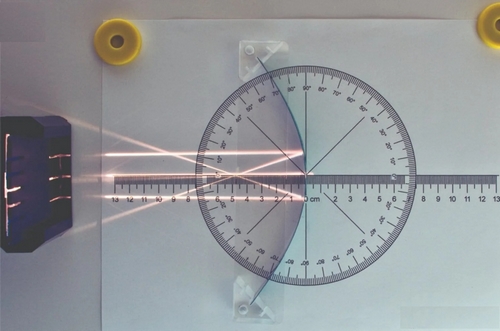
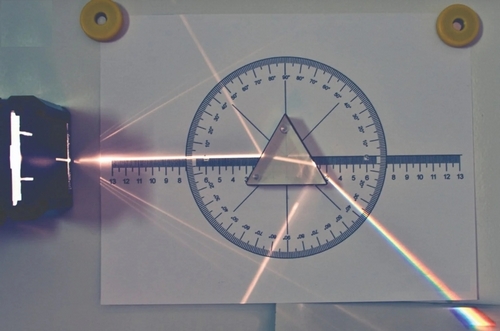
Optical Elements:
- All optical elements are 23 mm (⅞”) thick and have built-in fixing magnets and white-painted bottom surfaces (mirror holders unpainted)
- Lenses are 75 mm (3”) wide
- Rectangular block is 75 mm x 50 mm (3” x 2”)
- Prism sides: Equilateral: 60 mm (2⅜”) Right angle: 50 mm (2”) 30°-60°-90°: 38 mm—62 mm—73 mm (1½, 2⅜, 2⅞”) Plane mirror: 10 cm (4”) wide Adjustable concave/convex mirror: Width: 135 mm (5¼”) Approx. radii: 60 mm, 90mm, 170mm Rectangular trough: 75 mm x 50 mm (3”x 2”); Usable volume: 61 ml
- Refractive index of the acrylic material: approx. 1.49
Filters & Diaphragms:
- All filters and diaphragms are 62 mm (2⅜”) wide
- 1 blank diaphragm for blocking light in unwanted directions
- 2 diaphragms with narrow slits (1.28 mm/0.05” wide): One slit, two slits 28 mm/1.11” apart Three slits 14 mm/0.55” apart, five slits 8.5 mm/0.33” apart
- 1 diaphragm with a wide slit (9 mm/0.35”) and a 15mm/0.59” hole
- Set of 7 color filters: Red, green, blue, cyan, magenta, yellow, orange
- Set of 7 color paddles: Red, green, blue, cyan, magenta, yellow, orange
Targeted Gains:
- Explains the properties of lenses and lens types.
- Analyzes the variables that affect the focal length of a lens.
- Explores the properties of the image formed by the lenses.
- Discovers how light is refracted in concave and convex lenses.
- Finds the focal points of parallel light beams and thin and concave lenses.
- Gives examples of usage areas of lenses.
- Realizes that glass waste left in forest areas can pose a fire risk in sunny weather.
- Designs observation tools using lenses.
- Compares the similarities and differences of reflection and refraction of light.
Order & Discount Info:
- In order to be processed, your order has to be 45TL minimum.
- Shipping is free of charge for the orders 95TL and above.
- Shipping fee shall be 13.50TL for all orders below 95TL.
- 2% discount shall be applied for the orders paid via bank transfer and is 150TL and above.
- Payments can be made by credit card / debit card or money order / EFT.
- Payments made by credit / debit cards are processed by PayTR, a licensed payment institution operating within the framework of Law No. 6493
- Payments can be made in installments by credit card.
- Apart from our site, we also sell our products on n11.com, hepsiburada.com, and gittigidiyor.com. The price differences between the sites are due to the commission rates applied by the relevant platforms, the products shipped and the shipment time are the same.
Order & Discount Info:
- In order to be processed, your order has to be 45TL minimum.
- Shipping is free of charge for the orders 95TL and above.
- Shipping fee shall be 13.50TL for all orders below 95TL.
- 2% discount shall be applied for the orders paid via bank transfer and is 150TL and above.
- Payments can be made by credit card / debit card or money order / EFT.
- Payments made by credit / debit cards are processed by PayTR, a licensed payment institution operating within the framework of Law No. 6493
- Payments can be made in installments by credit card.
- Apart from our site, we also sell our products on n11.com, hepsiburada.com, and gittigidiyor.com. The price differences between the sites are due to the commission rates applied by the relevant platforms, the products shipped and the shipment time are the same.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.