Description
- It is prepared in ECE workshops under the supervision of the R&D team
- Compatible with the curriculum
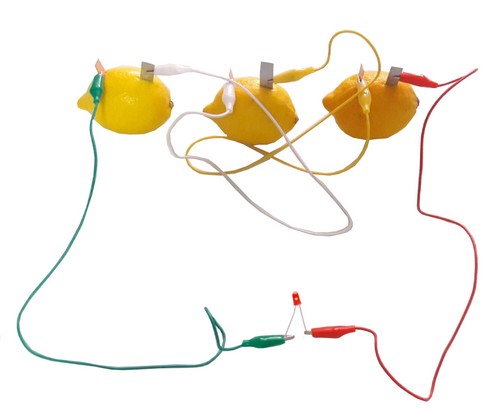
It is used in battery making experiments from fruits or vegetables (lemon, potato, etc.)
Product content:
- 3 copper plates measuring 0.6mm x 10mm x 50mm (99.99% electrolytic copper)
- 3 pieces of 0.6mm x 10mm x 50 zinc plates (Specific Gravity: 7.13g/cm³, Cu: 0.035%, Fe: 0.0019%, Mg: 0.0002, Sn: 0.0011, Pb: 0.0028 , Cd: 0.0001)
- 4 pieces of alligator cable
- 2 pieces of 5mm A quality LED diodes
- Number 0 sandpaper
- Printed application guide (Brief information about the experiment, how to conduct the experiment, the gains to be obtained from the experiment, questions to guide research on the experiment, questions to observe and benefit from the gains to be obtained from the experiment in daily life)
Targeted Gains:
- Designs and builds a simple electrical circuit to test whether substances transmit electrical energy.
- Classifies substances as conductors and insulators in terms of transmitting electrical energy.
- Realizes that some liquid substances are conductors and some are insulators.
- Realizes that the electrical conductivity and insulation properties of substances are used for various purposes.
- Realizes that electric current is a type of energy transfer.
- It means that electrical energy sources provide electrical current to the circuit.
Batteries, accumulators, etc. It measures the voltage between the poles of electrical energy sources using a voltmeter and states that the voltage unit is called volt. - Makes a battery from vegetables and fruits and observes that a chemical reaction turns into electrical energy.
- Researches how electricity can be produced using vegetables and fruits and zinc and copper electrodes.
- Observes that a chemical reaction turns into electrical energy.
- Understands the electrical circuit connection.
- Understands LED lamp feature









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.