Açıklama
- Ürün ECE kalite ve güvencesiyle ithalatımızdır
- Müfredatla uyumludur
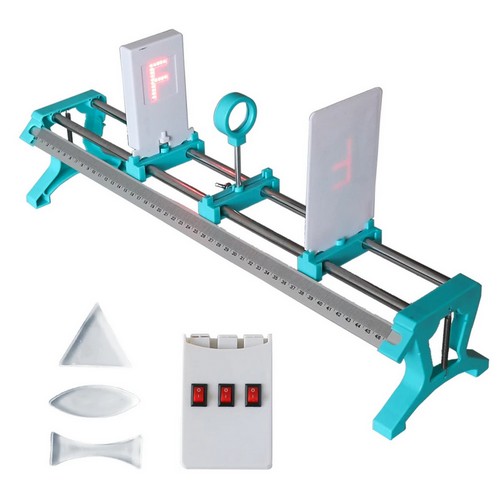
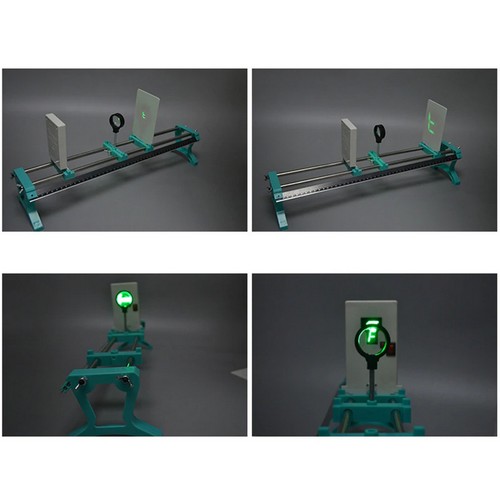
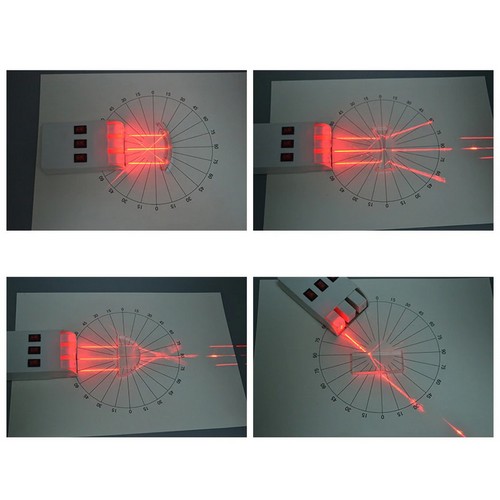
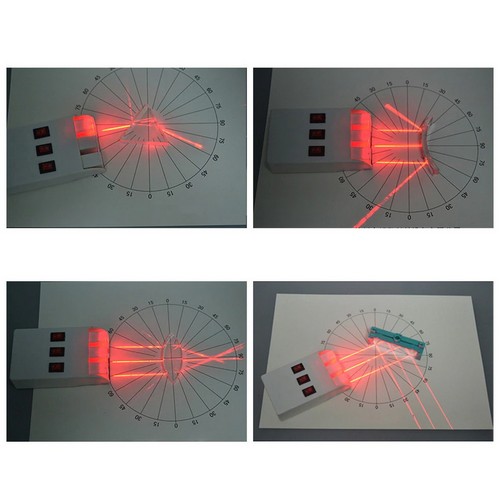
- Işığın yayılma yolu, ışığın yakınsaması, ışığın sapması, ışığın kırılması, ışığın düz yayılımı, iğne deliği görüntüleme, dik açılı yansıma deneyi, içbükey mercekle görüntüleme, dışbükey mercekle görüntüleme vb deneylerin yapılabileceği settir
- Deney setiyle gerçekleştirilebilecek uygulamalardan bazıları ürün sayfamızda bulunan videoda izlenebilir (dışbükey mercekle ters görüntü oluşturma, küçük delik görüntüsü oluşturma, içbükey ayna ile ışığın yakınsaması, içbükey mercekle ışığın sapma etkisi, dışbükey mercekle ışığın yoğunlaşma etkisi, yarım daire dışbükey mercekle ışığın yoğunlaşma etkisi, dikdörtgen blokla ışığın kırılması, üçgen prizma ile ışığın kırılması, aynasal yansıma, düzlem aynada görüntü oluşturma, ışığın üç ana rengi deneyleri)
- Ürünlerimizi TÜBİTAK, BİLSEM projelerinde ve kendi tasarımlarınızda güvenle kullanabilirsiniz
Ürün İçeriği:
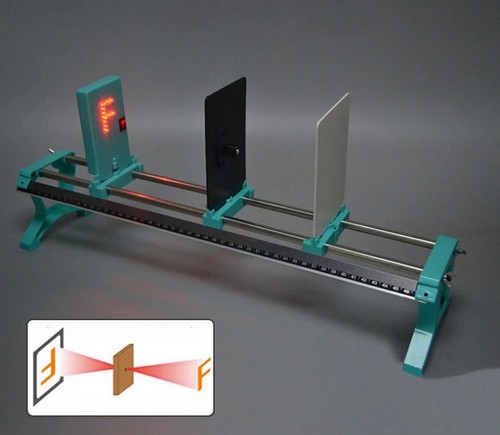
- Paslanmaz çelik ray (2 parça)
- Ölçekli cetvel (50cm)
- Kaydırıcı (3 adet)
- Ray taşıyıcı kaide (2 adet)
- Sabitleme vidası (2 adet. Kaydırıcıları sabitlemek için)
- Lazer (3’lü)
- F ışık kaynağı
- Elektronik mum
- Sink
- Üç ana renk
- Işık görüntüleme plakası (2 adet)
- Delikli plaka (Küçük delik görüntüsü oluşturma deneyi için)
- Renkli cam (Düzlem aynada görüntü oluşturma deneyi için)
- Dayanak (4 adet. F ve normal. Düzlem aynada görüntü oluşturma deneyi için)
- Dışbükey mercek (Saplı)
- İçbükey mercek (Saplı)
- Dikdörtgen blok
- Yarım daire blok
- Düzlemsel prizma
- Plano dışbükey mercek
- Plano içbükey mercek
- Düzlem ayna (2 adet. Dik açılı yansıma deneyi için)
- Silindirik kavisli ayna
- Açı plakası (Karton)
Hedeflenen Kazanımlar:
- Düz aynada görüntü oluşumunu çizerek açıklar.
- Küresel aynalarda odak noktası, merkez ve tepe noktasını kullanarak özel ışınları çizer ve görüntünün özellikleri hakkında çıkarımlar yapar.
- Kırılma kavramını açıklar ve kırılma olayına örnekler verir.
- Işığın tam yansıma olayını ve sınır açısını analiz eder.
- Işığın paralel yüzlü ortamdan geçerken izlediği yolu çizer ve bağlı olduğu değişkenleri açıklar.
- Farklı ortamda bulunan bir cismin görünür uzaklığını etkileyen sebepleri analiz eder.
- Merceklerin özelliklerini ve mercek çeşitlerini açıklar.
- Bir merceğin odak uzaklığını etkileyen değişkenleri analiz eder.
- Merceklerin oluşturduğu görüntünün özelliklerini keşfeder.
- Optik yasalarını kullanarak gözde görüntü oluşumunu açıklar.
- Optik aletlerin yapısını inceleyerek fonksiyonel bir optik alet tasarlar ve yapar.
- Işığın ince ve kalın kenarlı merceklerde nasıl kırıldığını keşfeder.
- Paralel ışık demetleri ile ince ve kalın kenarlı merceklerin odak noktalarını bulur.
- Işığın yansıması ve kırılması olaylarının benzerlik ve farklılıklarını karşılaştırır.
- Işığın madde ile karsılaştığında yansıyabileceğini keşfeder.
- Düz yüzeylerden yansıyan ışığın izleyeceği yolu tahmin eder.
- Işık kaynağı olmayan cisimlerin görülebilme nedenini ışığın yansımasıyla açıklar.
- Yansıma olayında; düzlem ayna kullanarak gelen ısın, yansıyan ısın ve yüzeyin normalinin aynı düzlemde olduklarını keşfeder.
- Yansıma olayında; düzlem ayna kullanarak gelme ve yansıma acılarının birbirine eşit olduğunu keşfeder.
- Düzgün ve dağınık yansımayı keşfeder.
- Cisimlerin daha parlak veya daha mat görünme sebeplerini ışığı yansıtma özellikleriyle ilişkilendirir.
- Düzgün ve dağınık yansımayı ışınlar çizerek gösterir.
- Işığın düz, çukur ve tümsek aynalarda nasıl yansıdığını keşfeder.
- Bir yüzeyden yansıyan ısınları gözlemleyerek ışığı yansıtan yüzey hakkında tahminlerde bulunur.
- Net bir görüntü oluşabilmesi için ışığın pürüzsüz yüzeylerden yansıması gerektiğini fark eder.
- Paralel ışık demetleri ile çukur ve tümsek aynanın odak noktalarını deneyerek keşfeder.
- Düz, çukur ve tümsek aynalarda oluşan görüntüleri cisme göre büyük-küçük, ters-düz olmaları bakımından karşılaştırır.
- Çevresinde kullanılan ayna çeşitlerini gözlemleyerek aynaların kullanım alanlarına örnekler verir.



 ECE Deprem Simülasyon Modeli Deney Seti Demonte
ECE Deprem Simülasyon Modeli Deney Seti Demonte  1.50mm x 25m ECE Emaye Kaplı Bakır Bobin Teli Ece Makarada
1.50mm x 25m ECE Emaye Kaplı Bakır Bobin Teli Ece Makarada  5 Adet 3V-12V DC 130 Motor Tamamen Metal Gövde A Kalite 6mm Mil
5 Adet 3V-12V DC 130 Motor Tamamen Metal Gövde A Kalite 6mm Mil  Polarizasyon Deney Seti Polarize Işık Optik Deneyi
Polarizasyon Deney Seti Polarize Işık Optik Deneyi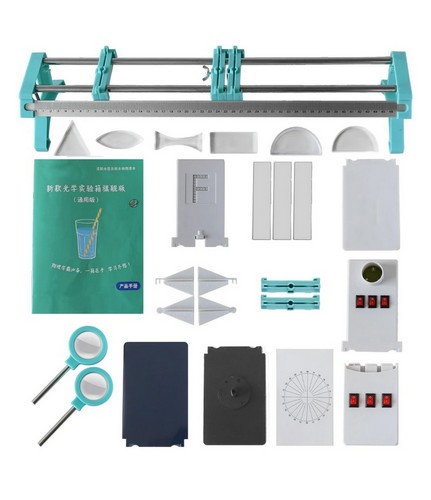 










İncelemeler
Henüz yorum yapılmadı.